This journal is brought to you by...
 I'm hold three amazing flags in front of Scott Base. Photo credit: Alex Eilers
I'm hold three amazing flags in front of Scott Base. Photo credit: Alex Eilers
- Michelle Wright and her 2nd grade class at Riverwood Elementary School
- Bilderback Home school
- Mefford's movie stars at Bon Lin Elementary School
I spy with my little – I mean – BIG eyes!
 What amazing eyes! Photo credit: Alex Eilers, MMPA Permit # 17411
What amazing eyes! Photo credit: Alex Eilers, MMPA Permit # 17411
The Weddell seals have big, brown, beautiful eyes. That’s one of the many reasons I love these amazing animals! And the seal pups have the most lovable eyes I’ve ever seen! Have you ever seen a cuter face?
 A beautiful Weddell seal and her very cute pup! Photo credit: Alex Eilers, MMPA Permit # 17411
A beautiful Weddell seal and her very cute pup! Photo credit: Alex Eilers, MMPA Permit # 17411
Weddell seal eyes are so big and pretty! They’re almost twice the size of human eyes. You might expect larger eyes in an animal much bigger than humans, but Weddell seals’ heads are about the same size as ours – so those eyes look really big! And what’s really cool about them is that they see on land and in the ocean. That’s like having two kinds of eyes!
Have you ever opened your eyes underwater? It wasn’t very comfortable, was it? And you probably couldn’t see very well. Humans aren’t made to see underwater, but Weddell seals can see better underwater than on land! So what’s different about Weddell seal eyes?
Let’s talk about eyes for a minute. The eye’s main job is to let light into it and then focus that light. Light is what allows you to see the world around you. Without light, you wouldn’t be able to see anything. That’s why you can’t see at night. This presents a problem for the Weddell seal – there is very little light deep in the ocean under the ice. So how do they see underwater? Their eyes have some special adaptations that are very different from our eyes, which make them perfect for seeing in low light.
The size
There is a big difference between our eyes and Weddell seal eyes – the size! Weddell seals have big eyes! An adult human eye is about 24 mm in diameter, which is about 1 inch or 2/3 the size of a ping pong ball. An adult Weddell seal’s eye is about 50 mm – twice as big, about the size of a hacky sack.
 What can you see up close? Photo credit: Patrick Robinson, MMPA Permit # 17411
What can you see up close? Photo credit: Patrick Robinson, MMPA Permit # 17411
These big eyes allow Weddell seals to take in more light.
The shape of the lens
Another big difference between our eyes and Weddell seal eyes is the shape of the lens. The lens is inside the eye and its job is to focus light – just like the lens on a camera. Check out the diagram below. The black part is the lens. Do you notice a difference between the shape of the seal (pinniped) lens and that of a human?
 See how the different shapes of the lenses make a difference in how we see. Photo credit: Alex Eilers
See how the different shapes of the lenses make a difference in how we see. Photo credit: Alex Eilers
The seal lens is very round, while the lens of a human is flattened and more oval-shaped.
When does near-sighted, far-sighted and normal vision occur?
Normal vision: When the focal points rests directly on the retina, not in front of or behind the retina.
Near-sighted vision: When the focal point is in front of the retina. Therefore, closer objects are clearer than objects that are far away.
Far-sighted vision: When the focal point rests behind the retina. This makes it easier to see distant objects and more difficult to see objects that are near.
Well, why is this important?
It comes back to light! Did you know that light bends? When light moves from one medium to another, it changes direction. Think about it like this – have you ever looked at a straw in a glass of water? It looks weird doesn’t it? That’s because light bends differently when it passes through water.
 Now remember, Polar bears do not live in Antarctica, but there are a couple at the Memphis Zoo and we took a field trip to see them! It’s not magic, but light bending! The polar bear looks distorted in this picture. Photo credit: Erika Ellis
Now remember, Polar bears do not live in Antarctica, but there are a couple at the Memphis Zoo and we took a field trip to see them! It’s not magic, but light bending! The polar bear looks distorted in this picture. Photo credit: Erika Ellis
The lens has to focus light onto the retina, which is at the back of the eye. When Weddell seals look through water, their round lenses will bend the light to focus the image on their retina. However, when looking through air, their round lenses bend the light so that its focal point is in front of the retina.
The result? Seals see really well in water, but not as well in air.
What else is different?
Seals may be a bit color-blind. The photoreceptor cells on the retina that ‘see’ color are called cones. Seals only have two sets of cones, while humans have three. So seals may have a difficult time seeing a variety of colors. However, they are most likely sensitive to blues and greens, which is good, because those are the main colors in their habitat!
Though the seals are missing cones, they have a lot of rods! Rods are a different set of photoreceptors that allow us to ‘see’ brightness. Since seals have so many, they can see very well at low light levels, which is great for seeing under the ice!
One more thing… Seals also have silvery, reflective layer behind their retina called a tapetum lucidem. This lining helps reflect light back onto the retina. Basically, this doubles the amount of light that the rods can ‘see.’ What other animals might have this tapetum lucidem?
 You make think this dog has laser eyeballs, but this is actually the reflection from the tapetum lucidem! Photo credit: Erika Ellis
You make think this dog has laser eyeballs, but this is actually the reflection from the tapetum lucidem! Photo credit: Erika Ellis
Many nocturnal animals have a tapetum lucidem. Have you ever seen an animal’s eyes shine when hit with a flashlight or the headlights of a car? What you are seeing is the reflection of the tapetum lucidem.
Clever creatures
Not only are Weddell seal eyes adapted to seeing in low light, but they have a few tricks up their sleeve as well! Scientists believe that they hunt fish by ‘back lighting’ them. But how do they do that? They will dive deep and look up to see a fish’s silhouette against the lighter surface waters. That’s just another way Weddell seals use their amazing eyes!
Sometimes Weddell seals look very sad – I thought this one was crying! But Dr. Burns reassured me that those aren’t tears! Weddell seals have a clear, protective mucus that covers their eyes. Scientists believe this washes away bacteria from the ocean water.
 Is this seal sad? Photo credit: Alex Eilers, MMPA Permit # 17411
Is this seal sad? Photo credit: Alex Eilers, MMPA Permit # 17411
Digging Deeper
Have you ever heard of snow blindness? It’s something we have to be very careful about here in McMurdo. The direct rays from the sun and those that reflect off the snow and ice can hurt your eyes. The ice in Antarctica works like a giant mirror. When light hits the ground here in Memphis, the ground absorbs the light. That’s why the sidewalk feels hot on sunny days. In Antarctica, the ice does not absorb the light, it reflects it. So, looking at all that reflected sunlight without sunglasses is a very bad idea! The ultraviolet B rays burn your eyes like they would burn your skin. It’s a bit like a sunburn – just on your eyes. It won’t actually make you blind, but it can be painful! To prevent this, we wear sunglasses or dark goggles out on the ice. Even humans that live in snowy environments, like the Inuit, have to protect their eyes.
Check out this photo!
 Inuit snow goggles made of wood with a sinew strap. Photo credit: Doctors of BC Medical Museum
Inuit snow goggles made of wood with a sinew strap. Photo credit: Doctors of BC Medical Museum
That got me thinking… I haven’t seen any seals wearing sunglasses, so how do Weddell seals protect their eyes?
Weddell seals have corneas that can tolerate high levels of UV light. The cornea is a squishy membrane on the outside of your eye.
So the light reflected off of the snow doesn’t give them any pain. That’s just another amazing feature about Weddell seals! They are much better adapted to living in this snowy environment than we are!
Want to know more about your eyes?
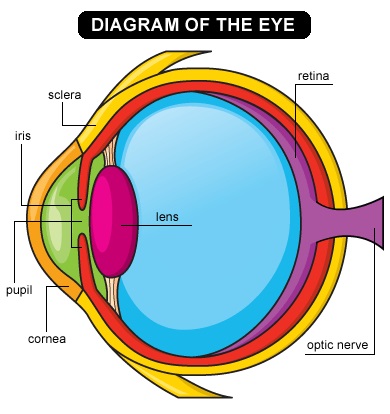 Diagram of the eye. Photo credit: Kids Health
Diagram of the eye. Photo credit: Kids Health
Your eye is an amazing organ with many different parts – all working together so you can see. Your eye captures and detects light.
When you look at an object, the light from it enters your eye through the pupil. The iris changes the size of your pupil, depending on how bright the object is. If it is very bright, your pupil gets smaller.
If it is darker, your pupil gets bigger. This allows your eye to take in more or less light. Have you ever noticed your pupils getting smaller or larger? How does that compare to the Weddell seals?
The light then hits your lens. The lens focuses the light onto the back of your eye – your retina. Have you ever looked behind you at a movie theater? There is a stream of light coming from the projection booth.
The lens of your eye works a lot like the lens of a movie projector. At the movies, the light goes through the lens, focusing the images onto the screen so that you can see the movie clearly. In your eye, the film screen is your retina!
The retina is a mass of photoreceptors called rods and cones, which are light-sensitive. Remember I talked earlier about the fact that Weddell seals have two sets of cones, but humans have three!
They change the light signals into electrical signals, which are carried to the brain by the optic nerve. Your brain interprets the electrical signals to figure out what you are seeing.
Pretty cool, right?


Comments